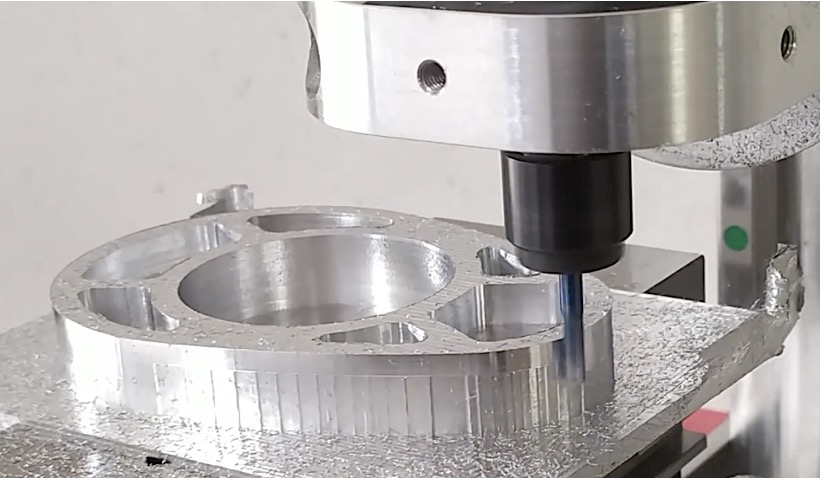

CNC machining is one of the most common types of conventional manufacturing technology generally associated with the machining of metals. CNC produces parts with high precision with applications across the industrial spectrum. Plastic materials are also CNC machined to produce high-quality parts. Design complexity increases the need for high precision, complex set-up preparation and programming etc. Here we are going to talk about the factors governing the cost of CNC machined parts.
There are no set of rules that can be applied to determine the cost of CNC, hence, it is important to understand the cost drivers which is key to many projects. Design, material, hardness, surface finish, equipment, production volume are a few of the important factors affecting the cost.
Tips to reduce the CNC machining cost
Design
Design and geometric complexity significantly affect the cost of CNC. Design complexity is directly proportional to the cost of CNC. Complex designs may need extra setup, programming time and special machine equipment, also, detailed inspection procedures. Certain design aspects that increase the cost of CNC like deep cavities, very high surface finish, thin walls are a few of the factors affecting the cost. Design aspects affecting the cost negatively should be avoided unless necessary or must be there. High surface quality and tight tolerance also add up to the cost.
Material Selection
Material selection is one of the most important cost drivers of CNC. The cost of material procured depends upon the type of material selected. For example, aluminum is costs less while titanium costs are much higher. Another important aspect of material selection is machinability. Hard to machine materials takes extra preparations, longer set-up times and consume more resources like extra fluids, power, and special cutting tools. The cost of a machined part is directly proportional to the time it takes to machine it.
Economies of Scale
we know that large scale production reduces the cost of the item. The same is true for the CNC parts. Cost per unit part is inversely proportional to the number of parts. The reduction in the cost is the result of savings realized in a one-time setup, CAD/CAM is handled only once for all the parts.
Surface Finishing
The surface finishing specification also determines the final cost of the part. CNC produces parts supposed to be used as it is, however, some specific applications may need post-processing procedures to attain desired surface quality like annealing, heat treatment, coatings etc. which will jack up the cost significantly. So, a designer needs to select the post-processing carefully according to the requirements.
Extra Tips –
- Add fillet in internal cavity edges – Sharp edges in the internal cavities are difficult to create because cutting tools are circular type. So, it is always recommended for a designer to apply radius at internal edges.
- Avoid thin walls – There’s a limit to a minimum thickness of the wall. The too-thin walls will lead to weak designs impacting the overall strength of the part. Refer to our CNC design guide for minimum wall thickness.
- Avoid nonstandard hole sizes – Nonstandard hole sizes may lead to extra machining time and costs because either a special tool needs to be procured or a special process to be carried out for non-standard hole making. It is better to keep standard holes size wherever possible.
- Restrict thread length – Keep adequate thread length needed to sustain the load/force on the design. Thread length beyond relevant requirements will add to extra costs.
- Add tolerances wherever needed – Unnecessary tolerance or too tight tolerances will lead to a major cost impact. Hence add tolerance wherever required to save on extra cost addition and time.
- Too many tool changes – Create a design that could be carved out with minimum tool changes. This strategy will not only save costs but also machining time.
- Aesthetics – It is best to go for post-processing (polishing, coating etc) to achieve the desired surface quality than thru the machining process. Achieving it thru the machining process will not only add to the cost but also complicate the machining process.
- Part set-up – A designer should also think about how the part is going to be fixed onto the machine bed. A complicated fixture set-up will add up the costs but also increase the lead time significantly. Because extra time is needed to manufacture the holding fixture.
Conclusion
CNC machining is the widely used conventional manufacturing process that can create parts with a high degree of accuracy and repeatability with close tolerances. However, just following a few cost reduction tips, a designer can not only save on costs but also the lead time.
Blog created by - 3D SculpLab Team


 3D SculpLab
3D SculpLab