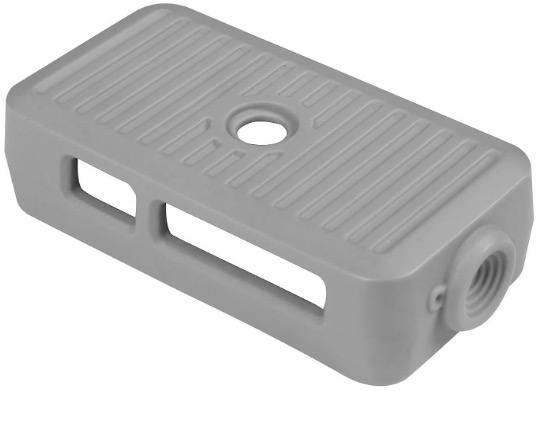

Vacuum casting is the manufacturing process of creating parts thru silicon made mold. VC is generally preferred for low-volume production of parts and rapid prototyping. VC working concept is the same as injection molding, both use a mold, however, the manufacturing process differs significantly from injection molding. VC has a wide range of available materials (ABS, polypropylene, nylon, polycarbonate, flexible) to choose from with varying properties from plastics to flexible. VC produces parts with appearance, mechanical properties and surface finishes comparable to those made with injection molding. The detailed process steps are described below.
Video credits: SCOTTAM
Pattern Making
A pattern is a physical part created out of the CAD data received from the customer. The pattern is either created by 3D printing or CNC machining.
Silicon mold making
The pattern is kept inside the casting frame and then liquid silicon is poured over it. Once cured, the mold is divided into 2 halves and the pattern is recovered.
Casting process
Polyurethane mixture is prepared according to the desired proportions and then poured into the mold. The mixture then takes the shape of the cavity inside the mold and is then cured inside a vacuum chamber. The vacuum inside the chamber sucks out all the air bubbles to ensure a smooth finish part.
Key Advantages of Vacuum Casting
1. Lower production cost – VC production cost is generally lower compared to CNC which is a subtractive type manufacturing technology. CNC machining leads to material wastage plus stock preparation & setup time also adds up to the total cost. In VC, there’s no such material wastage except the silicone mold which is discarded after the process ends.
2. Fast turnaround – The silicon mold could be prepared in a day once the pattern is available and can make out around 20 parts. VC can achieve continuous production and is a time-saving process in companions to CNC & injection molding.
3. Replicate properties of actual material – VC can make prototypes in the same material they are supposed to be produced during mass production. Vacuum casting creates the same effect as other manufacturing ways. VC can simulate most of the mechanical and functional properties like smoothness, rigidity & flexibility as per final design intent. Example- Acrylic(PMMA) for testing light transmission, ABS for high impact strength, EPDM for flexibility.
4. Thin-walled parts – Thin-walled parts consume less raw material and could be useful under certain conditions. Also, light in weight. It is difficult to produce parts with thin-walled by conventional manufacturing due to machine/process limitations.
5. Uniform part quality – Vacuum casting ensures that every part has the features of the same shape, size, finishing, thickness etc. Uniform part quality and quick turn-around makes vacuum casting an ideal choice for short-run production
6. High-quality surface finish – Desired surface finish could be achieved either by pre-processing the pattern (3D printing, CNC) surface or post-processing the casting part thru painting, polishing etc.
Drawbacks
1. Plastics only – VC can replicate properties of plastic materials only. Not available for metals due to higher casting temperature of metals (over 600˚C) than VC (200˚C – 400˚C). Silicon mold will simply melt away at higher temperatures for metal casting.
2. Pattern glitch – Unlike 3D printing & CNC machining where every part is checked for flaws, in VC that is not the case because if the pattern was created with flaws same will reflect on the casting part. This risks higher rectification costs & time over-runs.
3. Unsteady tolerances – After curing, silicon mold shrinks around 2% average pressing against the pattern. Shrinkage helps the mold in taking the accurate shape of the pattern, but this also leads to loose tolerance in the VC part. It is up to the molding expert to predict shrinkage & accordingly cast the parts. VC is not recommended for parts requiring tight tolerances.
4. Short mold life – Due to short lifespan, silicon mold worn out quickly after casting a number of parts. Hence, new mold needs to be made for additional products which are time-consuming and add extra costs.
5. Hollow cavities – If the silicon mold is not filled properly or air got trapped inside the mold, then the casting part is rejected and need to be re-cast. The vacuum chamber resolves most of the bubble issues but still depends upon the operator skill to minimize the risk of cavities.
Conclusion
Vacuum casting is widely used for short-run production, prototyping, and functional testing. Due to fast turnaround, costs low against CNC & 3D printing, VC is recommended for engineers, startups who want realistic looking parts with functional properties and shortened iteration time.
Blog created by - 3D SculpLab Team


 3D SculpLab
3D SculpLab